Home > What we do > Observations > Satellite Observation
Meteorological satellites help to visualize atmospheric condition, including clouds in a real-time basis. The satellite observation has been used for not only weather forecasting, but also climate change detection and atmospheric research. With the advance of sensor technology, the temporal, spatial and spectral resolution of satellite observation continues to be improved.
KMA receives the data from three geostationary satellites, including MTSAT-1R, Meteosat-7 and FY-2C, and several polar orbiters, such as NOAA, Aqua/Terra, FY-1D and MetOp in a real-time basis.
The data has been used to generate various meteorological products, for example, atmospheric motion vector, sea surface temperature, fog/stratus, Asian dust, cloud information, etc. The products as well as imagery data are distributed to forecasters and users through Internet and Intranet, as soon as processed. Some of these products are also ingested into the data assimilation of NWP models.
Fog detection
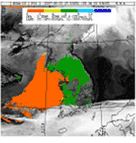
Asian dust detection
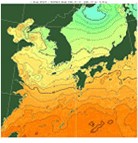
Sea Surface Temperature
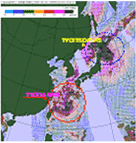
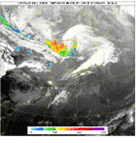
Typhoon monitoring
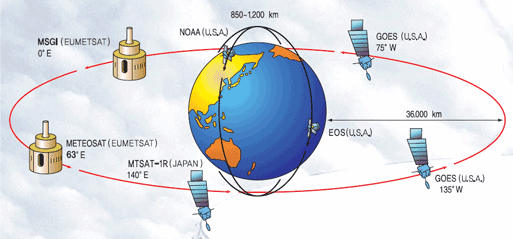
Global Satellite Observation Network


COMS (Communication, Ocean and Meteorological Satellite), Korea's first multi-purpose geostationary meterological satellite, will be launched in 2009. For the reception and processing COMS data, a ground system has been established, since 2005. The Korea Meteorological Satellite Center/KMA will carry out the meteorological mission of COMS.
For the meteorological services, the full disk will be observed every 3 hours, and three different regional observations will be done every 30 minutes, respectively. In case of severe weather occurring in and/or approaching to the Korean peninsula, special observation mission will be given to watch the severe weather phenomena. The interested area may be scanned as frequent as once per 10 minutes.
For the maximum benefit from the COMS observation, up to 16 meteorological products will be generated. The products range from cloud information to atmospheric motion vector, sea surface temperature, and Asian dust, etc., and are under development by the National Institute of Meteorological Research/KMA.
An aerial view of korea Meteorological Satellite Center